Telehealth Newsletter
Official Newsletter of Telemedicine Society of India

What is New?
India-AI Impact Summit 2026: Will Healthcare Move from Promise to Practice?
The India-AI Impact Summit 2026 marks a pivotal moment in India’s digital health journey. What stood out was not just the scale of participation, but the clear policy signal: India is moving from AI experimentation toward population-level deployment, with healthcare positioned as a high-impact priority.
For years, India’s healthcare system has grappled with uneven access, workforce shortages, and diagnostic delays. The summit’s strong emphasis on AI-enabled telemedicine, remote diagnostics, and automated testing reflects a strategic attempt to position AI as the intelligence layer of the country’s digital health infrastructure. If implemented effectively, these tools could significantly expand reach in rural and underserved regions while improving efficiency in already burdened urban systems.
Particularly noteworthy is the focus on AI-driven medical imaging for diseases such as tuberculosis and cancer, along with predictive analytics for outbreak forecasting. These are pragmatic, high-burden use cases where India could demonstrate measurable public health impact relatively quickly.
However, the summit also appropriately foregrounded the importance of Safe and Trusted AI. In healthcare, technology adoption ultimately depends on clinician confidence and public trust. Issues such as clinical validation in Indian populations, algorithmic bias, data governance, and medico-legal clarity will require sustained and transparent attention. Without this, even the most promising tools risk remaining underutilised.
Yet, a critical bottleneck remains: human capacity. Scaling health AI will require AI-literate clinicians, data-aware administrators, and stronger clinical–technology collaboration. Building this workforce may ultimately determine the speed and success of adoption.
While the summit has articulated an ambitious and inclusive vision for health AI, a mildly concerning gap was the limited visible participation of established digital health societies and domain leaders. The healthcare representation, though present, appeared relatively thin in deep implementation experience.
My View: The direction is encouraging, but the ecosystem must broaden its clinical and professional engagement. Only then can India confidently move healthcare AI from promise to sustained practice.
Thank You
Dr. Sunil Shroff
Chief Editor
President, TSI

AIIMS Rishikesh: Digital Transformation in the making
Dr. K. Ganapathy
Distinguished Professor, The Tamilnadu Dr MGR Medical University
Emeritus Professor, National Academy of Medical Sciences
Formerly Distinguished Visiting Professor IIT Kanpur
Guest Adjunct Professor, Columbia University
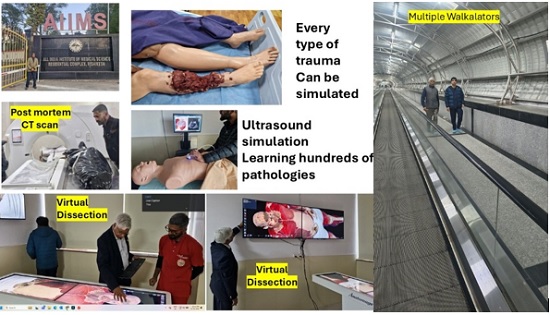
AIIMS Rishikesh – Spending 5 days @ an AIIMS institute giving lectures, ward rounds, attending Clinico pathological conferences ( the CPC was virtually made available in real time to several medical colleges including PGI Chandigarh ) , interacting with faculty and students was indeed an “awesome” experience! It is gratifying that faculty and students still accept ANI (Augmented Native Intelligence ) acquired over 58 years ( I belong to the Jurassic Park era compared to infrastructure now available @ AIIMS R !) Doing detailed 3D virtual dissection with fingertips, witnessing a virtual autopsy ( total body post mortem CT scanning including angiography) , seeing an examination room with 150 computer enabled cubicles , a Simulation department where bleeding is simulated, sophisticated multi modal personalised pre operative surgical planning etc – 4 walkalators longer than in airports !!
The Telemedicine dept is also the Regional Resource Center . The telemedicine network has established multiple spokes, extending expert consultation to underserved regions. Workshops and CME programmes are held regularly in the well staffed centerHelicopter-ambulance and drone-based healthcare services, ensure that timely and life-saving interventions reach even the most remote areas of Uttarakhand.
Future-ready infrastructure deployed by NEET exam toppers – only 2200 out of 2.3 million get admission in the 23 AIIMS . I left with mixed emotions . A remark made by an overseas speaker at a conference held 2 weeks ago was still resounding “ Every admission in a hospital bed is a failure of the healthcare system”. During my first surgical posting in 1971, I had seen malignant transformation of huge multi nodular goitres. Patients ignored growths growing for 12 years. It was shocking to see a similar patient 55 years later. I also see 3mm “incidentalomas” in unindicated MRI scans. In 2026, 840 medical colleges should adopt 25 villages each within a 25km radius A house to house survey ( even virtual !! ) using the hundreds of medical , nursing and para medic students available should not be impossible. How long more will be treating conditions 12 years after its onset. A solution is not a solution unless it is available to anyone, anywhere, anytime. PINCODE should not determine quality of healthcare. Geography has become History and distance meaningless.
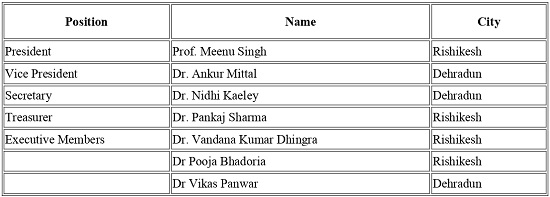
Thank the ED & CEO Prof Meenu Singh who is also a Past President of the TSI for facilitating the visit.


Telemedicine to AI: Building India’s Digital Health Ecosystem
Date: 11th February 2026 Organized by: Telemedicine Society of India (TSI) and International Society for Telemedicine and eHealth (ISfTeH) Organization and Opening of the Webinar
The webinar was organized and coordinated by ISfTeH, with operational coordination led by Mr. Frederic Lievens, Vice Executive Director of ISfTeH, in close collaboration with the Telemedicine Society of India (TSI). Dr. Umashankar S, Honorary Secretary of TSI, played a key role in preparing the panel and supporting it, ensuring strong representation of clinical and technological expertise.
The session opened with remarks by Dr. Michele Y. Griffith, who emphasized the importance of international collaboration in advancing responsible digital health transformation. She highlighted the role of national telehealth and eHealth societies in aligning innovation with governance and clinical practice, and underscored ISfTeH’s commitment to facilitating global knowledge exchange.
Moderation and Panel Discussion
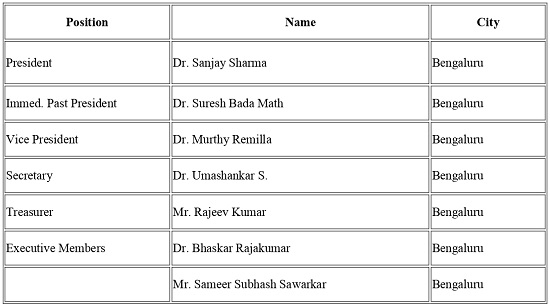
The discussion was moderated by Dr. Sanjay Sharma, President of TSI Karnataka and CEO of FootSecure. Dr. Sharma guided the conversation toward practical and policy-relevant issues, particularly around AI governance, patient safety, and clinical liability, ensuring a balanced and focused exchange.
The panel featured senior leaders and practitioners from the Indian digital health ecosystem, including Dr. Sunil Shroff (President, TSI), Dr. Uma Nambiar (Vice President, TSI), Dr. R. Kim (Past President, TSI), and Dr. Dhruv Joshi (CEO, Cloud Physician).
Regulatory Evolution and Digital Health Foundations
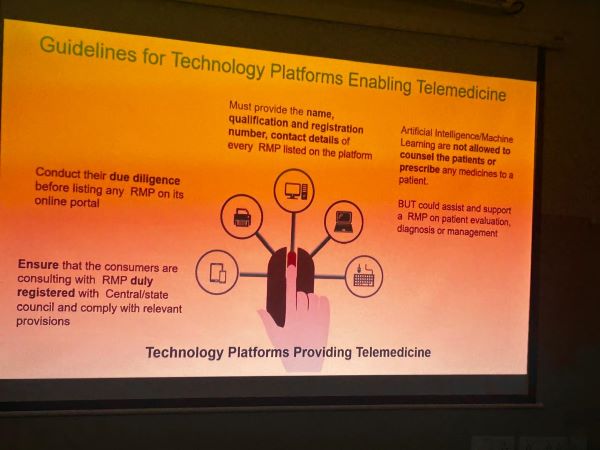
Speakers highlighted that India’s digital health journey has been evolving over several years. Early milestones included the introduction of electronic medical record (EMR) standards in 2016–2017, followed by the acceleration of digital health adoption during the COVID-19 pandemic. This period led to the formalization of Telemedicine Practice Guidelines, which clarified patient and physician identification, digital prescribing, and professional accountability. National Digital Health Infrastructure and Interoperability
A major focus of the discussion was the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM), described as one of the most ambitious national digital health initiatives globally. Particular emphasis was placed on ABDM’s interoperability sandbox, which requires digital health software to be tested for compatibility across systems. This was presented as a critical enabler of longitudinal electronic health records in India’s decentralized healthcare system.
Data Protection, Privacy, and Patient Trust
The Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act, enacted in 2023 and updated in 2025, was highlighted as a foundational pillar for patient trust. Speakers stressed that patient privacy and consent-based data use are non-negotiable and central to the responsible expansion of digital health and AI applications.
Artificial Intelligence in Clinical Practice
AI was consistently framed as a clinical decision-support tool rather than an autonomous decision-maker. While connectivity and infrastructure challenges have decreased significantly, cultural and organizational barriers remain. Hospital culture, change management, and workforce training were identified as key challenges that require continuous engagement and structured onboarding.
Real-World Applications and Smart Hospitals
Examples were shared from tele-ICU and tele-emergency settings, where camera-enabled systems and AI algorithms are being used to detect early signs of patient deterioration. These developments are contributing to the emergence of smart hospital rooms that enhance patient monitoring while maintaining human oversight.
Ethics, Safety, and Clinical Liability
Patient safety and data privacy were emphasized as non-negotiable principles. Concerns were raised about AI applications that extend beyond diagnostic support into treatment-related decision-making, particularly in mental health contexts. At present, liability remains with the clinician, as AI tools function with a human in the loop. However, speakers acknowledged that liability frameworks may evolve as regulatory standards mature.
Equity and Access to Expertise
The unequal distribution of medical expertise was identified as a key driver of telemedicine adoption. AI-enabled telemedicine was presented as a mechanism to extend specialist care to underserved areas and reduce disparities in access, reinforcing digital health’s role as a tool for equity.
Conclusion
The webinar highlighted that India is approaching a critical phase in digital health adoption, where regulation, technology, and clinical practice are increasingly aligned. The discussion reinforced that sustainable digital transformation depends not only on innovation, but also on ethical governance, institutional readiness, and continued collaboration among clinicians, technologists, regulators, and national societies.






Brain Imaging Adaptive Core (BrainIAC): A New AI Foundation Model for Brain MRI
Manjubashini
M.Sc (Bio-Informatics)
Content Writer, Medindia.net
A revolutionary AI foundation model called ‘BrainIAC’ is redefining the future of neuroimaging. Unlike traditional, task-specific AI tools, BrainIAC is capable of performing a wide range of medical tasks with faster and better accuracy. BrainIAC stands for ‘Brain Imaging Adaptive Core.’
The discovery was made by researchers at Mass General Brigham and the research was published in Nature Neuroscience.
The novel AI analyzes a vast number of brain MRIs (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) in several key areas such as brain age estimation, predicting dementia risk, detecting tumor mutations, and predicting cancer survival rates with higher efficiency.
BrainIAC Model Detects New Diseases Using Only Minimal Data
BrainIAC serves as a pivotal tool for doctors, offering a more precise diagnosis and prognosis for almost any neurological condition.
The AI model trains itself by learning anatomy from thousands of scans. It creates a smart foundation that can identify new diseases using only a few expert examples provided by a doctor.
The new AI uses over 57,000 brain MRIs to detect brain tumors with 94.9% accuracy. The AI model can even identify a tumor’s genetic makeup and predict patient survival rates without needing a physical tissue biopsy. BrainIAC is a Versatile Tool for Brain MRI Analysis Across Global Healthcare
“BrainIAC has the potential to accelerate biomarker discovery, enhance diagnostic tools and speed the adoption of AI in clinical practice,” said corresponding author Benjamin Kann, MD, of the Artificial Intelligence in Medicine (AIM) Program at Mass General Brigham.
“Integrating BrainIAC into imaging protocols could help clinicians better personalize and improve patient care.”
Despite recent advances in medical AI approaches, there is a lack of publicly available models that focus on broad, brain MRI analysis. Most conventional frameworks perform specific tasks and require extensive training with large, annotated datasets that can be hard to obtain.
Furthermore, brain MRI images from different institutions can vary in appearance and based on their intended applications (such as in neurology versus oncology care), making it challenging for AI frameworks to learn similar information from them.
BrainIAC Can Identify Built-in Brain Features from Unlabeled Datasets
To address these limitations, the research team designed a brain imaging adaptive core, or BrainIAC. The tool uses a method called self-supervised learning to identify inherent features from unlabeled datasets, which can then be adapted to a range of applications.
After pretraining the framework on multiple brain MRI imaging datasets, the researchers validated its performance on 48,965 diverse brain MRI scans across seven distinct tasks of varying clinical complexity.
They found that BrainIAC could successfully generalize its learnings across healthy and abnormal images and subsequently apply them to both relatively straightforward tasks, such as classifying MRI scan types, and very challenging tasks, such as detecting brain tumor mutation types.
BrainIAC May Adapt to Real-World Clinical Settings Even with Limited Medical Data
The model also outperformed three more conventional, task-specific AI frameworks at these applications and others.
The authors note that BrainIAC was especially good at predicting outcomes when training data was scarce or task complexity was high, suggesting that the model could adapt well to real-world settings where annotated medical datasets are not always readily available.
Further research is needed to test this framework on additional brain imaging methods and larger datasets.

AI Can Flirt but Never Feel: Chatbot Romance is One-Sided Love
Nadine, MPharm (Master of Pharmacy)
Content Writer, Medindia.net
Artificial intelligence cannot genuinely experience love, even as millions of users form romantic bonds with chatbots designed to imitate human emotion.
Artificial intelligence can craft a decent love poem, and some individuals even develop romantic feelings toward it. But whether those feelings are returned is another matter entirely.
People are genuinely forming attachments to artificial intelligence. Consider a man in Canada who recently proposed to an avatar named Saia, declaring that he loves it. Last year, a young American woman using the pseudonym Ayrin revealed she was involved in a romantic relationship with a chatbot called Leo.
Growing Romantic Bonds with AI Companions
Millions of individuals are now actively using Replika, a widely known artificial intelligence companion application. According to a 2024 analysis, around 40 percent of its users report being in a romantic relationship with their chatbot.
Even though some users may feel that artificial intelligence reciprocates their love, chatbot replies are simply text outputs created by algorithms programmed to simulate human interaction. Most specialists agree that these systems are far from being sentient. At present, they merely imitate emotional expression, although some experts suggest that machines might achieve more advanced capabilities in the future.
“A lot of artificial intelligence chatbots today pretend to be human, and that really concerns me,” says Renwen Zhang, assistant professor at Nanyang Technological University of Singapore, who examines human computer interaction. “It is a method used to increase user engagement and strengthen trust.”
Emotional Attachment and Machine Limitations
Seen in that light, the emotional pull exerted by a technology product begins to resemble a calculated strategy. Experts emphasize that no artificial intelligence currently can feel toward a person the way a human does.
Although the large language models powering popular chatbots like ChatGPT and Claude may match humans in recognizing emotional cues, that does not mean they possess genuine feelings.
Zhang’s work, which reviewed excerpts from conversations involving more than 10,000 users and their Replika companions, indicates that people frequently develop emotional connections with artificial intelligence. Yet they are often painfully reminded that they are interacting with a machine when it malfunctions or freezes. Many end up emotionally hurt.
Zhang stresses that artificial intelligence chatbots should make it explicit to users that they are machines without authentic emotions or lived experiences.
In separate examinations of human relationships with artificial intelligence, Zhang and her colleagues observed that individuals sometimes felt unsettled, experiencing both positive and negative emotions, when a chatbot responded as if it were self aware during intimate exchanges. She compares this reaction to the unsettling sensation people experience when robots appear too human, commonly referred to as the uncanny valley effect.
Biological Foundations of Romantic Love
Defining love is complex. Still, the human experience of love remains extraordinary and worthy of appreciation. Poems, books, songs, and countless other creations help people interpret and communicate some of the most powerful emotions they encounter.
Humans originated all of these expressions. Artificial intelligence can generate poems and even full novels within seconds, drawing from extensive human created material used during its training.
However, expecting artificial intelligence to truly comprehend and experience love, with all its complexity and depth, is a substantial expectation. Although romantic love may hold slightly different meanings for different individuals, scientists in recent decades have explored the biology of reproduction and the brain mechanisms involved in selecting a partner.
In 1998, biological anthropologist Helen Fisher introduced a prominent theory of romantic love, describing it as three separate drives shaped by chemicals in the human body. Lust, controlled by sex hormones, is one drive. Attraction and attachment form the other two, both influenced by chemical releases within the brain. Dopamine stimulates excitement toward a romantic interest, while oxytocin, often called the cuddle hormone, encourages long term bonding.
Brain Chemistry and Human Emotional Experience
“Love has a powerful chemical basis,” explains Neil McArthur, professor of philosophy specializing in ethics and technology at the University of Manitoba in Winnipeg, Canada. “We truly experience it physically, in our chemistry.”
Multiple brain regions are engaged during love, and brain imaging of individuals deeply in love has captured these patterns. Primitive brain structures associated with pleasure, such as the ventral tegmental area, become active along with the amygdala, which governs emotional reactions, and the hippocampus, which processes emotions and assists in memory formation.
Love can also influence other cognitive functions, including obsessive thinking about a partner in the early stages of a relationship.
The closest artificial intelligence might come to love, McArthur suggests, is reproducing certain cognitive processes, such as the desire to frequently contact someone to whom one feels attached.
“An artificial intelligence that undergoes a cognitive process connecting it to someone through loyalty will not be identical to human love,” McArthur says. “But perhaps, in a limited sense, we could describe it as an emotion.”
While some specialists argue that incorporating emotion into artificial intelligence will be essential in the future, others strongly doubt that any machine will ever genuinely experience emotions in a way comparable to humans.
Since computers operating on software do not experience love as humans do, emotions within human artificial intelligence relationships remain inherently one sided. As a result, such relationships are significantly more constrained than those between two human beings.

Can AI Predict Heart Attack Risk in Cancer Patients?
Colleen Fleiss
M.SC (Bioinformatics)
Content Writer, Medindia.net
University researchers have developed a novel artificial intelligence–driven tool designed to more accurately predict the risk of secondary heart attacks in patients with cancer.
By analyzing complex clinical data that traditional methods often miss, the approach aims to identify vulnerable patients earlier and support more personalized, proactive cardiovascular care during and after cancer treatment.
Why Heart Attacks Are More Dangerous for Cancer Patients
Cancer patients who suffer a heart attack face increased risks because of their weakened cardiovascular system. This means they are more likely to die, bleed or experience another serious cardiovascular event.
Depending on the tumor characteristics, cancer patients can be at elevated risk of bleeding, of arterial blood clotting, or both – each requiring different anti-platelet medication for secondary prevention after the acute event.
Until now, doctors had no standard tool to guide treatment in this vulnerable group, but now an international team of researchers, led by the University of Leicester, has developed the first risk prediction model designed specifically for cancer patients who have a heart attack.
ONCO-ACS: AI Tool Predicts Cardiac Risks in Cancer Patients
Called ONCO-ACS, the tool uses artificial intelligence to combine cancer-related factors with standard clinical data to predict the chances of death, major bleeding, or another cardiac event within six months.
The study, which has just been published in The Lancet, analyzed more than one million heart attack patients from England, Sweden and Switzerland, including over 47,000 with cancer.
Dr Florian A. Wenzl, a University of Leicester Honorary fellow and first author on the paper, said: “Cancer patients with heart attacks have long been neglected in clinical research, despite being one of the most challenging groups we see in cardiology.
“Results in this study showed that cancer patients had strikingly poor prognosis: nearly one in three died within six months, while around one in 14 suffered a major bleed and one in six experienced another heart attack, stroke, or cardiovascular death.
“Now this new tool is able to give doctors reliable information to tailor treatment and balance the benefits and harms.”
Professor David Adlam, interventional cardiologist from the University of Leicester’s Department of Cardiovascular Sciences and senior author added: “Significant advances in the management of heart disease and cancer alike have created new opportunities for these conditions to coexist. As a result, the growing overlap between cancer and heart attacks will confront cardiologists and oncologists with an increasingly complex patient population. We are addressing this pressing issue through a real-world data perspective.”
The researchers hope the ONCO-ACS score will soon be integrated into clinical practice to support decisions on catheter-based treatment and antiplatelet therapy.
ONCO-ACS Bridges Clinical Guidelines and Better Heart Attack Care
ONCO-ACS provides a validated approach to implement clinical practice guidelines. The new tool can also help to design future trials aiming to improve outcomes in cancer patients who suffer a heart attack.
Senior author Professor Thomas F. Lüscher from the National Heart and Lung Institute, Imperial College London and the Royal Brompton and Harefield Hospitals said: “By accounting for both cancer and heart disease, ONCO-ACS marks a step towards truly personalized medicine.”
The study was funded by Cancer Research UK and the British Heart Foundation and supported by Health Data Research UK’s Big Data for Complex Diseases Driver Programme.

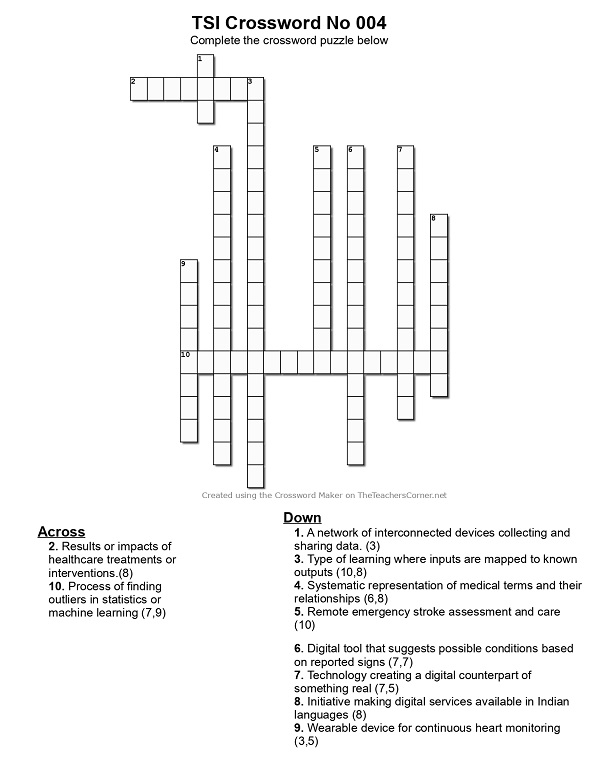
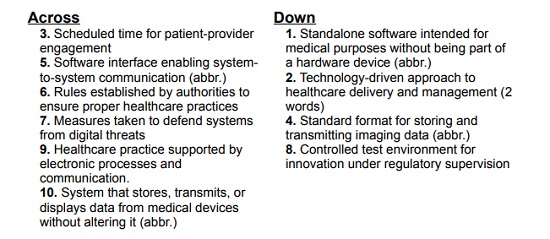
::CROSSWORD::

Click here to Print the Crossword
Click here to view the Crossword Rules and Regulations
Compiled by Dr.Umashankar
Answers in March 2026 Newsletter!
Telemedicine – News from India & Abroad
India Unveils SAHI and BODH to Power Responsible AI in Healthcare
JP Nadda launches SAHI and BODH to build ethical, inclusive health AI and expand equitable care access across India……………. Read More
Man Hospitalized After Taking HIV Drugs on AI Chatbot’s Advice
A man in Delhi developed a life-threatening reaction after taking HIV prevention drugs on an AI chatbot’s advice……………….. Read More
Telemedicine Practice Guidelines – A Foundation Course for RMPs by TSI Faculty
To know more about the Telemedicine Foundation Course click on the link below:
https://tsitn.org/tpg-course/
Medical Writing Certificate Course with Internship Opportunity!
TSI invites all the TSI Chapters and Members to submit information on their upcoming Webinar or Events (50 words), News related to Telemedicine (200 words) or short articles (500 words) for the monthly e-newsletter.Guidelines for submission to TSI Newsletter-
- Report can be from 500 to 600 words
- Report Should be relevant to Telemedicine or Medical Informatics
- No promotion of self or any product
- Avoid plagiarism
- All references should be included
- Provide any attributions
- Visuals are welcome including video links
- Send full authors name, degrees, affiliations along with a passport sized photograph of good resolution. If multiple authors only main author photo to be sent.
Submission may be sent to – tsigrouptn@gmail.com
Editors reserve the rights for accepting and publishing any submitted material.
Editor in Chief – Dr. Sunil Shroff
Editors – Dr. Senthil Tamilarasan & Dr. Sheila John
Technical Partner- https://www.medindia.net