Telehealth Newsletter
Official Newsletter of Telemedicine Society of India

What is New?
In 2023, global temperatures reached the highest on record since 1850, at 1.18°C above the 20th-century average of 13.9°C. This surpassed the previous 2016 record by 0.15°C. The ten warmest years have all occurred in the last decade (2014-2023). With 2024’s summer expected to set new records, more people may turn to telehealth, a trend I’ve observed in my practice over the past four years.
This issue features an excellent piece from Dr. Ganapathy and Dr. Umasankar’s report on a webinar with Ayushman Bharat. Tamil Nadu and Uttarakhand chapters have excelled in promoting telehealth. Dr. Arti Pawaria has launched a commendable 6-month online course with TSI on Nutrition in Clinical Pediatric Practice for Pediatricians, Nutritionists, and Pediatric Trainees.
We look forward to our mid-term meeting on 21st June in Dharamsala, where we plan to officially launch our newsletter under the national banner.
Thank You
Dr. Sunil Shroff
Chief Editor
Vice President, TSI
::TSI Activities from Around the Country::

Telemedicine on Ships
Dr. K. Ganapathy
Distinguished Visiting Professor IIT Kanpur | Distinguished Professor The TamilnaduDr MGR Medical University | Emeritus Professor National Academy of Medical Sciences | Past President : Telemedicine Society of India, Neurological Society of India, Indian Society for Stereotactic & Functional Neurosurgery | Formerly WHO Digital Health Expert | Director Apollo Telemedicine Networking Foundation & Apollo Tele Health Services
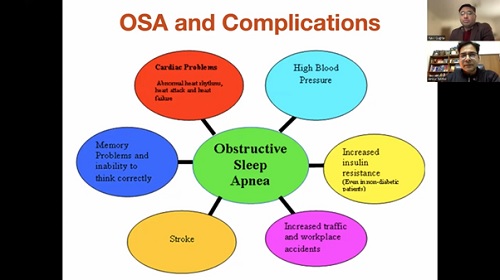
It is often forgotten that instant access to healthcare is critical in remote isolated locations and areas. Interestingly a phenomenal amount of money and resources are being spent to keep humans on board the ISS (International Space Station) orbiting 400 km above the earth. Health issues of all the 280 humans from 23 countries who have been living in the ISS for the last 24 years ( periods varying from few weeks to several months ) have been addressed and managed.
Air travel today is no longer a luxury. In India, 4.17 lakh passengers board 2891 flights every day. No doubt In Flight Medical Emergencies occur rarely – 7 per 10,000 passengers leading to unscheduled landing (1 for 1 million passengers). Unnecessary diversion causes flight hazards, inconveniences, ↑fuel ↑costs.
Provision of In Flight Emergency Medical Services could therefore be a tremendous value addition. 15 years ago in my enthusiasm as a Telemedicine evangelist I made presentations to the CMO’s of three airlines including the then progressive Jet Airways and even the Director General of Civil Aviation. Perhaps the credibility of the institution which I was associated with and my personal credentials enabled a hearing!! Permission could not be obtained to include Telemedicine equipment in aircrafts for pilot studies. Attempts to do pilot projects on ships also did not materialise then.
It was therefore gratifying to learn that today much water has flown under the bridge (pun intended!). International Labour Organisation (ILO) & Maritime Labour Convention states “—–provide seafarers with medical care as nearly as possible equivalent to care on shore, and to ensure that medical advice by radio or satellite communication to ships at sea is available at any hour of the day or night”. Every ILO signatory nation is bound to have a prearranged system for wireless medical advice available to ships of all nationalities, round the clock and free of charge, also known as Telemedical Assistance Services(TMAS). This network ensures communication through marine radio, email, telephone or fax and in more recent times, via real-time video calls.
The author thanks the Tamilnadu Chapter of the TSI and Amet University for the opportunity given to revive an important topic, not in the main stream of Telehealth.

The Impactful Work of TSI, Tamil Nadu Chapter: Raising Awareness Among Engineering Students – Part 2
Mr. D. Satheesh Kumar, M.Sc (IT), MBA, DECE.
Honorary Secretary–TSI, Tamilnadu Chapter
As many in the telemedicine industry know, the Tamil Nadu Chapter of TSI has been actively engaged in a variety of telemedicine initiatives. One of our key efforts has been raising awareness among engineering students by organizing telemedicine conferences over the past eight years at various engineering colleges in Tamil Nadu, including VIT University, KCG College of Technology, RMK Engineering College, Panimalar Engineering College, and Priyadharshini Engineering College.
An interesting event took place in April 2024. After concluding our third telemedicine conference at KCG College of Technology, we received a call from a university authority who invited us to conduct a conference at his university. This invitation was promptly accepted by Dr. T. Senthil, Vice-President of TSI, Tamil Nadu Chapter.
Typically, we reach out to institutions to request their participation in our telemedicine conferences. However, due to the success of previous events, such as those at RMK Engineering College and KCG College of Technology, the demand for discussions on telemedicine grew among engineering colleges. Consequently, AMET University, known for its unique maritime academy courses, extended an offer to host a telemedicine conference.
Despite the challenge of presenting to students not focused on core engineering subjects like Electrical, Electronics, BME, IT, or CS, we accepted the offer and quickly organized the event. With Dr. Sashilatha, Dean of International Relations at AMET University, coordinating as the Telemedicine Conference Convener, everything was arranged professionally, including invitations, program schedules, and technical arrangements.
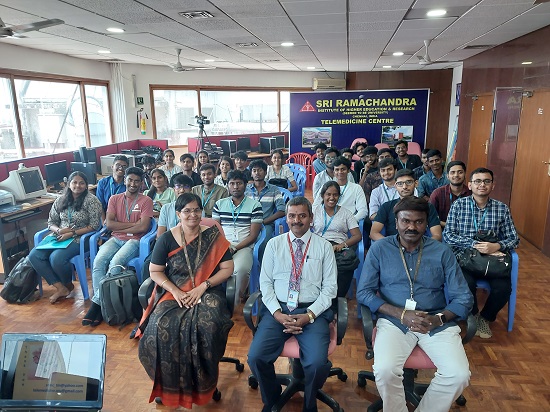
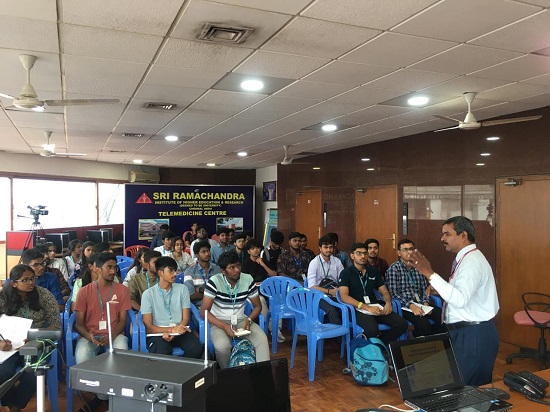
On April 26, 2024, we held a one-day telemedicine conference titled “Innovations in Telemedicine Technology” at Sri Janakiram Auditorium, AMET University, Chennai, with 300 students and faculty members in attendance. Seven speakers, including three in-person and four online presenters from Chennai, Madurai, Hosur, and Bengaluru, delivered insightful lectures.
I began the conference with an “Overview of Telemedicine,” covering the basics, concepts, purposes, principles, setups, technology, and opportunities, which served as a foundational introduction. Dr. T. Senthil’s presentation on “Role of Tele-ophthalmology” captivated students by showcasing high-resolution fundus photos and discussing remote handling of ophthalmic issues during ship travel.
Dr. Sheila John from Sankara Nethralaya provided an extensive online lecture on tele-ophthalmology practices, emphasizing that distance, whether on land or sea, is not a barrier to treatment. Dr. K. Ganapathy’s much-anticipated talk on “Telemedicine in Ships” highlighted the application of telemedicine on Earth, Sea, and Orbit, sharing his own experiences in remote high-altitude regions.
Mr. Napolean P.C.’s practical session on “Engineering & Demo of TM App” demonstrated telemedicine’s accessibility to the general public. Mr. Aswin Desai, MD of A&T Video Network, inspired students with his extensive experience in telemedicine, including the installation of telemedicine equipment on ships.
Dr. Sanjay Sharma concluded with a powerful lecture on “Role of AI in Wound Care,” showcasing live demonstrations of AI applications in surgical care, which greatly impressed the students.
This event was a unique and enriching experience for both the engineering students and us. It underscored the relevance of telemedicine across various fields, including maritime studies, and highlighted the importance of continuous learning and adaptation in this rapidly evolving industry.
Our President, Dr. Ikramulla H., also delivered an inspiring speech on Humanoid Robots and the telemedicine industry, which left a lasting impression on the attendees.




Transforming Healthcare: Navigating the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM)
Dr. (Prof.) Umashankar S.
Managing Director Med.Bot | Hony. Secretary, TSI- Karnataka Chapter & TSI Hqrs, Lucknow
Webinar on Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM)
Telemedicine Society of India in its constant endeavor to keep members informed about the various initiatives in the healthcare ecosystem, organized an exclusive webinar jointly with the National Health Authority (NHA), MoHFW, on Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM) on 30 April 2024 from 3:00 PM to 4:30 PM. This event brought together nearly 375 registered participants, including TSI members, doctors, educators, digital health companies, telemedicine service providers, hospital administrators, and technology enthusiasts from different parts of India to discuss the importance of ABDM.
The webinar kicked off with a welcome note by Dr Umashankar S, Honorary Secretary of the TSI, and opening remarks by Dr R Kim, the President of the Telemedicine Society of India. DrKim Spoke about how ABDM will be the backbone of the digital health infrastructure of the country and some of the benefits and challenges. Mr. Neel Ratan, Advisor NHA Enlightened the participants on the overall scheme of ABDM, its benefits, and its application in different use cases.
Following that, there were 4 presentations
Advantages of ABDM for key stakeholders by Mr Himanshu Dhingra, Senior Consultant, National Health Authority
Relevance of ABDM for telemedicine & UHI as a use-case by Ms Devika Bhatia, Product Manager, National Health Authority
Demonstration of National Healthcare Providers Registry (NHPR) by Mr Kunal Arora, Program Manager, National Health Authority
Overall ABDM Integration by Dr Raunaq Pradhan, Product Lead, National Health Authority.
Participants actively engaged with the speakers during the Q&A session, posing insightful questions about implementing ABDM. Key concerns such as data security, training, and interoperability, including telemedicine service providers, to effectively use ABDM were thoroughly discussed.
The webinar received overwhelmingly positive feedback from participants, who appreciated the informative content and practical insights. Many attendees expressed interest in more frequent webinars and deeper explorations of specific digital health and telemedicine topics.
The Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM) webinar was a resounding success, providing valuable knowledge on ABDM. The Telemedicine Society of India plans to continue this initiative by organizing follow-up sessions and specialized workshops, further supporting stakeholders in navigating and implementing ABDM and reap the benefits for better patient care. This event highlighted the transformative power of digital health and ABDM in healthcare and set a foundation for ongoing dialogue and professional growth in this vital area.


Webinar on Epilepsy unveiled
Dr. (Prof.) Meenu Singh
Executive Director & CEO
All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Rishikesh, Uttarakhand | President, TSI- Uttarakhand Chapter & Chandigarh Chapter and Past President – TSI
The Telemedicine Society of India (TSI), Uttarakhand State Chapter, continued its monthly initiative to propagate medical education on important topics by hosting a webinar on “Epilepsy unveiled.” This report summarizes the key aspects covered in the webinar, including medical and surgical management of epilepsy, the diagnostic challenges and the outcomes of various treatment modalities.

Epilepsy, a chronic neurological disorder characterized by recurrent seizures, affects millions of people worldwide. While seizures can be effectively controlled with medication in many cases, a significant portion of patients experience drug-resistant epilepsy. This necessitates exploring alternative management strategies, including surgery. This report delves into the medical and surgical approaches for managing epilepsy.

The webinar boasted the combined attendance of both Neurology as well as Neurosurgery departments to present the medical and surgical management respectively for epilepsy.
We started with Neurology team discussing about the basic definition, classification and pathogenesis of epilepsy. Case based informative videos were used to show the actual symptoms of various forms of epileptic disorders so that our upcoming healthcare professionals could develop better understanding of the topic. Emphasis was laid on careful and detailed history taking for better prognostication and asserting various treatment modalities to the patients. Then we proceeded to understand the medical management of epilepsy.

Medications remain the cornerstone of epilepsy treatment. The goal is to find an anti-seizure medication (ASM) or combination that effectively prevents seizures with minimal side effects. The selection of an ASM depends on various factors like seizure type, cause of epilepsy, individual tolerability, and potential interactions with other medications.
Various ASMs discussed included:
Sodium channel blockers: Examples include Lamotrigine, Carbamazepine, and Phenytoin.
GABAergic drugs: Examples include Gabapentin, Levetiracetam, and Zonisamide.
Other mechanisms: Topiramate
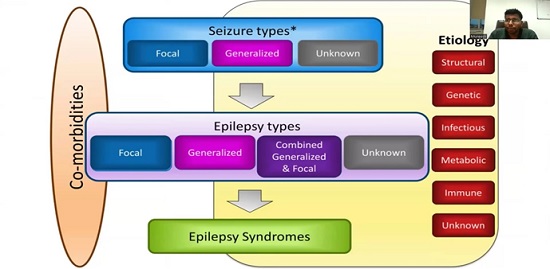
Next, we discussed on the treatment initiation and monitoring regimens where we concluded that the guidelines were to start with a single ASM at a low dose and gradually increase it to achieve seizure control. Regular monitoring of seizure frequency, blood levels of the medication, and potential side effects was crucial.If a single medication failed to control seizures, a combination of two or more ASMs with different mechanisms of action was warranted. However, this would increase the risk of side effects and the complexity of medication management.
In some cases, additional medications would be used to manage specific seizure types or address co-existing conditions like anxiety or depression.
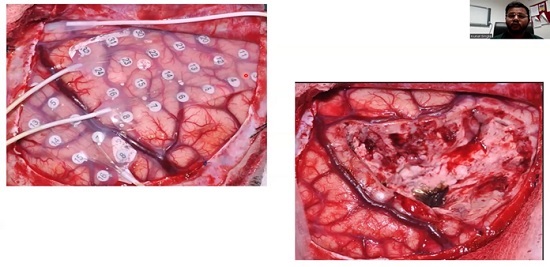
Further, we talked upon the surgical management of epilepsy where Neurosurgery department commenced by enumerating various surgical techniques available including the ones from the past to the recent advances. Ideal candidates for epilepsy surgery included those having seizures originating from a well-defined area of the brain (focal epilepsy) that can be safely removed without causing significant functional deficits. Pre-surgical evaluation involved extensive testing, including neuroimaging (MRI), electroencephalography (EEG), and neuropsychological assessment.
Various surgical techniques discussed included broadly:
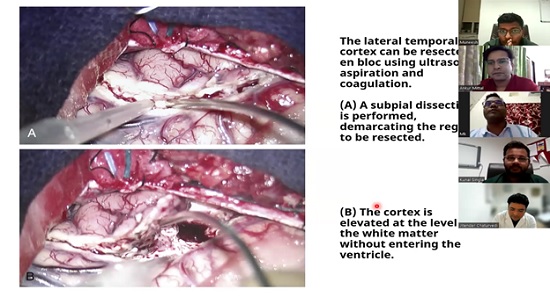
Resective surgery:the most common type of epilepsy surgery, involving the removal of a small portion of the brain containing the seizure focus. The specific type of resection depended on the location of the seizure focus. Examples include temporal lobectomy (removal of part of the temporal lobe) and frontal lobectomy (removal of part of the frontal lobe).
Disconnective surgery: Aiming to disconnect the pathways between seizure-generating areas and other parts of the brain, thereby preventing seizure spread. Corpus callosotomy is an example, where surgeons sever the corpus callosum, the main bundle of nerves connecting the two hemispheres of the brain.
Minimally invasive surgery: Newer techniques like laser interstitial thermal therapy (LITT) use lasers to destroy the seizure focus with minimal tissue damage were also discussed.
Potential complications that were discussed included bleeding, infection, and neurological deficits depending on the location of the surgery.
The concluding remarks emphasized the importance of proper history taking and dedicated workup before assigning any treatment modality to the epileptic patients. The webinar served as providing continued medical education in understanding the technical aspects and guidelines regarding epilepsy management and the recent updates and innovations regarding the same.

Nutrition in Clinical Pediatric Practice: A 6-Month Online Course for Pediatricians, Nutritionists, and Pediatric Trainees
Dr. Arti Pawaria
MD Pediatrics
PDCC Ped Gastroenterology
DM Ped Hepatology and Transplant
Clinical Lead Senior Consultant, Dept of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology & Liver Transplantation, Amrita Institute of Medical Sciences, Faridabad, Delhi NCR.
The Telemedicine Society of India (TSI) is proud to present an overview of flagship continuing medical education (CME) initiative: “Nutrition in Clinical Pediatric Practice.” This 6-month online course, tailored for pediatricians, nutritionists, and pediatric trainees, aims to significantly contribute to enhancing the nutritional knowledge and practices of healthcare professionals involved in pediatric care. Here, we reflect on the achievements and impact of this program over the past year.
Course Overview and Objectives
The “Nutrition in Clinical Pediatric Practice” course is meticulously designed to provide comprehensive education on pediatric nutrition. The course aims to:
Enhance Knowledge: Provide in-depth knowledge about pediatric nutrition, including essential nutrients, dietary requirements, and nutritional assessment techniques.
Improve Clinical Skills: Equip participants with the skills necessary to apply nutritional principles in clinical settings to improve patient outcomes.
Update on Latest Research: Keep participants informed about the latest research and advancements in pediatric nutrition.
Facilitate Professional Development: Support the continuous professional development of pediatricians, nutritionists, and pediatric trainees through an accessible and flexible learning platform.
Curriculum and Structure
The course curriculum is structured into various modules, each focusing on critical aspects of pediatric nutrition. The modules include:
Basic Nutritional Science: Covering the fundamentals of nutrients, their functions, and dietary sources.
Growth and Development: Understanding the nutritional needs at different stages of child development.
Nutritional Assessment: Techniques and tools for assessing the nutritional status of pediatric patients.
Clinical Nutrition: Addressing nutrition in specific clinical conditions like obesity, undernutrition, and chronic illnesses.
Public Health Nutrition: Exploring the role of nutrition in public health and preventive pediatrics.
Each module is delivered through a combination of video lectures, interactive webinars, case studies and practical assignments, ensuring a comprehensive and engaging learning experience. Participants have access to a wealth of resources, including reading materials, recorded session sand discussion forums.
Impact and Outcomes
Since its inception, the course has witnessed substantial participation from healthcare professionals across the country. The following are key highlights and outcomes from the past year:
Participant Demographics: The course attracted over 50 participants, including pediatricians, nutritionists, and pediatric trainees from various regions.
Feedback and Satisfaction: Participant feedback has been overwhelmingly positive, with 90% rating the course as “excellent” or “very good” in terms of content quality, relevance, and delivery.
Knowledge Gain: Pre- and post-course assessments indicate a significant improvement in participants’ knowledge and understanding of pediatric nutrition, with average scores increasing by 30%.
Clinical Application: Participants reported increased confidence in applying nutritional principles in their clinical practice, leading to improved patient care and outcomes.
Conclusion
The “Nutrition in Clinical Pediatric Practice” course has been a landmark initiative by the Telemedicine Society of India, contributing significantly to the professional development of pediatric healthcare providers. The positive feedback and tangible outcomes reflect the course’s success in enhancing the nutritional care of pediatric patients.
As we move forward, TSI remains dedicated to expanding and improving this program, ensuring that our healthcare professionals are well-equipped with the knowledge and skills necessary to provide the best possible care for children. We look forward to a year of impactful learning and improved pediatric health outcomes through our continued efforts in telemedicine-based education.
::ANNOUNCEMENTS::

About the speaker
Dr. K. Ganapathy, well known as a pioneer in Telemedicine is currently associated with educational activities. He serves as a Distinguished Visiting Professor at IIT Kanpur; Distinguished Professor at The Tamilnadu Dr MGR Medical University; Emeritus Professor at National Academy of Medical Sciences; and Guest Adjunct Professor at Columbia University. Formerly, he was an Adjunct Professor at IIT Madras, & Anna University; an Honorary Consultant and Advisor in Neurosurgery Armed Forces Medical Services.
He is the Past President of the Telemedicine Society of India, the Neurological Society of India and the Indian Society of Stereotactic and Functional Neurosurgery.
In 1990, Dr. Ganapathy became the first in South Asia to get a Ph.D. in neuro-imaging. First neurosurgeon from South Asia to be trained in Stereotactic Radiosurgery in 1995 and later in robotic radiosurgery in 2008. He ventured into Telehealth in 1998.
During the last 49 years, he has presented 616 papers in national conferences and 202 in international conferences, published 133 scientific papers, 208 articles in magazines and newspapers and 24 chapters in text books. He had served as the guest editor for three special supplements of a national and international journal and has also edited a book on Health IT.
He is Member of the Editorial Board of 4 International and 3 National Journals in Telemedicine and Neurosciences. Additionally, he is on the editorial board of 8 and reviews articles for 17 national and international journals.
As a former member of the Program Advisory Committee Dept of Science & Technology and member of BIRAC (Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council) Committee, Govt of India, he has considerable experience in reviewing research projects for funding. He was also on the WHO Roster of Experts on Digital Health. He is on the Board of Directors of the Apollo Telemedicine Networking Foundation and Apollo Telehealth Service. For his full CV please refer https://kganapathy.in
About the presentation
Deployment of 5G is leading to a significant transformation of many industries. Traditionally the healthcare “industry” is conservative. Concurrently, there is considerable hype and aggressive promotion of 5G as a use case in healthcare.
This presentation will give a broad overview of the entire landscape of a current topic of interest, highlighting use, challenges and potential of 5G in healthcare. Real world applications of 5G in healthcare and use of Edge Computing with 5G will be presented. 5G will also be compared with 4G and 6G. Specific clinical applications such as use of 5G in simulation labs, tele-mentoring, telesurgery, medical imaging, pre hospital management and use of robots will be touched upon.
While concrete evidence that deployment of 5G actually betters individual health care outcomes is awaited, the information available today justifies preliminary trials using 5G in a controlled environment. The presentation will also address on the challenges in deploying 5G in a healthcare setting.
Please register at https://bit.ly/49VgDnE

Telemedicine – News from India & Abroad
Artificial Intelligence Revolutionizes the Future of Cancer Therapy
Health experts noted that AI plays an important role from developing new drugs to predicting the treatment outcome and prognosis……Readmore
Bluetooth Tracking Devices Redefine Care Home Standards
Wearable Bluetooth devices offer insights into the care provided to residents in care homes, identifying those requiring increased social interaction………Readmore
Pediatricians Vs. ChatGPT: Assessing Developmental Delays
Cease seeking developmental assessments from ChatGPT for your child. Recent research indicates that AI tools such as ChatGPT…..Reademore
Role of Artificial Intelligence in Alleviating Mental Health Burdens
Artificial Intelligence (AI) holds the potential for providing psychological first aid to address India’s growing mental health concerns……. Readmore
TSI invites all the TSI Chapters and Members to submit information on their upcoming Webinar or Events (50 words), News related to Telemedicine (200 words) or short articles (500 words) for the monthly e-newsletter.Guidelines for submission to TSI Newsletter-
- Report can be from 500 to 600 words
- Report Should be relevant to Telemedicine or Medical Informatics
- No promotion of self or any product
- Avoid plagiarism
- All references should be included
- Provide any attributions
- Visuals are welcome including video links
- Send full authors name, degrees, affiliations along with a passport sized photograph of good resolution. If multiple authors only main author photo to be sent.
Submission may be sent to – tsigrouptn@gmail.com
Editors reserve the rights for accepting and publishing any submitted material.
Editor in Chief – Dr. Sunil Shroff
Editors – Dr. Senthil Tamilarasan & Dr. Sheila John
Technical Partner- https://www.medindia.net

























































 9. Himachal Pradesh Chapter on May 13, 2023: With active support and lead role by Dr. Vikrant Kanwar of AIIMS Bilaspur and wishes of Dr. Vir Singh Negi, Executive Director AIIMS, Bilaspur, the HP chapter was inaugurated on May 13, 2023. This is personally special and dear to me as this is my birthday celebrated in a satisfying way with the inauguration of a new chapter in an important hilly state of India. Dr. Vikrant also came to Telemedicon2022 at Goa and joined a parallel meeting with me along with Dr Arti Pawaria of Haryana and got motivated to form a state chapter and continued the work soon after going back. Another pleasant news is the state chapter soon after formation has come forward to host 2024 Telemedicon at HP in Dharamshala (Kangda) in Nov 2024 which was ratified by the 2023 AGM.
9. Himachal Pradesh Chapter on May 13, 2023: With active support and lead role by Dr. Vikrant Kanwar of AIIMS Bilaspur and wishes of Dr. Vir Singh Negi, Executive Director AIIMS, Bilaspur, the HP chapter was inaugurated on May 13, 2023. This is personally special and dear to me as this is my birthday celebrated in a satisfying way with the inauguration of a new chapter in an important hilly state of India. Dr. Vikrant also came to Telemedicon2022 at Goa and joined a parallel meeting with me along with Dr Arti Pawaria of Haryana and got motivated to form a state chapter and continued the work soon after going back. Another pleasant news is the state chapter soon after formation has come forward to host 2024 Telemedicon at HP in Dharamshala (Kangda) in Nov 2024 which was ratified by the 2023 AGM.

 11. Jharkhand Chapter on Aug 18, 2023: With active support and membership drive by Dr.Maishraj of AIIMS Deogarh, the Jharkhand chapter of TSI was inaugurated on Aug 18, 2023 under the aegis of President TSI Dr. Meenu Singh and Dr. Saurabh Varshney, Director AIIMS.
11. Jharkhand Chapter on Aug 18, 2023: With active support and membership drive by Dr.Maishraj of AIIMS Deogarh, the Jharkhand chapter of TSI was inaugurated on Aug 18, 2023 under the aegis of President TSI Dr. Meenu Singh and Dr. Saurabh Varshney, Director AIIMS.
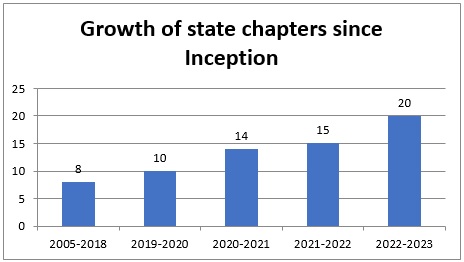
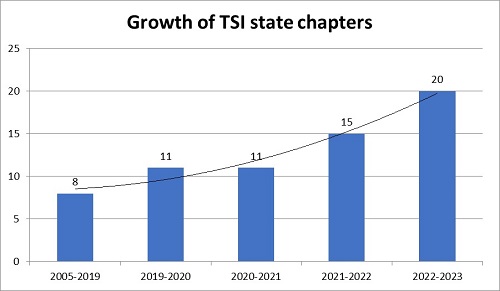 Though the growth of state chapters across the regions is increasing and pleasant to be noted, more and more activities are expected to be taken up under the aegis of these chapters with active participation by more members and particularly the younger generation. While conducting online/offline seminars and workshops or trainings is an initial and minimal activity to be taken up, the next and expected step in the journey is conducting some remote/rural camps with real usage and utilization of Telemedicine in practice.
Though the growth of state chapters across the regions is increasing and pleasant to be noted, more and more activities are expected to be taken up under the aegis of these chapters with active participation by more members and particularly the younger generation. While conducting online/offline seminars and workshops or trainings is an initial and minimal activity to be taken up, the next and expected step in the journey is conducting some remote/rural camps with real usage and utilization of Telemedicine in practice.



 Quiet unexpectedly but most pleasantly, the state chapter within a period of 9 months from the formation, came forward to successfully host the mid-term conference of 2022 on Aug 26, 2022 again at the prestigious SKIMS. The participation of several young doctors and particularly students and their presentation of high quality research papers was an added attraction in the mid-term conference.
Quiet unexpectedly but most pleasantly, the state chapter within a period of 9 months from the formation, came forward to successfully host the mid-term conference of 2022 on Aug 26, 2022 again at the prestigious SKIMS. The participation of several young doctors and particularly students and their presentation of high quality research papers was an added attraction in the mid-term conference.















 Dr. Selvakumar: Thanks to dr ratta Speakers were off high quality Introduction of dr Ganapathy for quiz was amazing Time management personally by dr ratta was super Food quality was very tasty and rich started by exacises to reduce my calories Overall the the conference was of 7 star ratting Exhibit showcasing was in par excellent ENTERTAINMENT WAS SUPER WITH FUN THANKS to dr ratta again single man show lessons to be learnt from him how to manage such conferences My sincere thanks and appreciattin to old EC team with spl thsnks to dr murthy for excellent management for the last 4 yrs Welcome to the new EC team ism sure this team will tske to greater heights with leadership of dr kim Members absence was only defect in telelmedicon confrence atl we should have double the attendance Nothing more can be done by the TSI in showcasing yearly event I thsnk all the members who attended for the grouth of TSI the meet with there support.
Dr. Selvakumar: Thanks to dr ratta Speakers were off high quality Introduction of dr Ganapathy for quiz was amazing Time management personally by dr ratta was super Food quality was very tasty and rich started by exacises to reduce my calories Overall the the conference was of 7 star ratting Exhibit showcasing was in par excellent ENTERTAINMENT WAS SUPER WITH FUN THANKS to dr ratta again single man show lessons to be learnt from him how to manage such conferences My sincere thanks and appreciattin to old EC team with spl thsnks to dr murthy for excellent management for the last 4 yrs Welcome to the new EC team ism sure this team will tske to greater heights with leadership of dr kim Members absence was only defect in telelmedicon confrence atl we should have double the attendance Nothing more can be done by the TSI in showcasing yearly event I thsnk all the members who attended for the grouth of TSI the meet with there support. Dr. Raj Raval, Gujarat Chapter of TSI: On behalf of TSI GUJARAT CHAPTER, I’m thanking Dr.Ratta sir for involving us in organising squad although he knows he was very much able to do own his own. We learnt lot many things from him. He literally took all the pains to deliver wonderful event to us. Contents, New ideas pitching, timings, industries participation, food , cruise….everything were fabulous.
Dr. Raj Raval, Gujarat Chapter of TSI: On behalf of TSI GUJARAT CHAPTER, I’m thanking Dr.Ratta sir for involving us in organising squad although he knows he was very much able to do own his own. We learnt lot many things from him. He literally took all the pains to deliver wonderful event to us. Contents, New ideas pitching, timings, industries participation, food , cruise….everything were fabulous. Dr. Satyamurthy: You are incredible Dr.Selva. Nice to see your remarks. Dr.Ratta was the dream boy organiser of utmost sincerity, commitment and recorded his hattrick of conducting 3 TSI conferences with grand finale of taking you all on Cruise ship which I missed. God bless our group young Margadharshaks.
Dr. Satyamurthy: You are incredible Dr.Selva. Nice to see your remarks. Dr.Ratta was the dream boy organiser of utmost sincerity, commitment and recorded his hattrick of conducting 3 TSI conferences with grand finale of taking you all on Cruise ship which I missed. God bless our group young Margadharshaks.